Research Topic: Quantitative Biomechanical Analysis of Biped Locomotion – Capture of Human Motion
Accurate quantification of kinematics (locomotion) represents a significant requirement for the purpose of physical rehabilitation in medicine, designing of prosthesis in orthopedics, analysis and optimization of sporting disciplines, researches in bio-mechanics, humanoid robotics, etc.
Bio-inspired locomotion of biped robots (humanoids) is based on a sophisticated analysis of human motion. For this purpose, a variety of experimental measurements have been done in the capture motion studio. For that purpose, specialized software (MSHUB - Software interface for Modeling and Simulation of HUman Bio-mechanics) for processing and interpretation of experimental results (measurements) has been developed. In the laboratory conditions, a set of the extensive experiments have been done, measuring motion characteristics (using corresponding fluorescent markers and 6-infra red cameras) as well as ground reaction forces and torques (by the 6-axis force platform, Fig. 1). Bio-mechanical measurements were performed in cooperation with colleagues at University of La Reunion, Faculty for Sport and Physical Activities, Le Tampon, France.
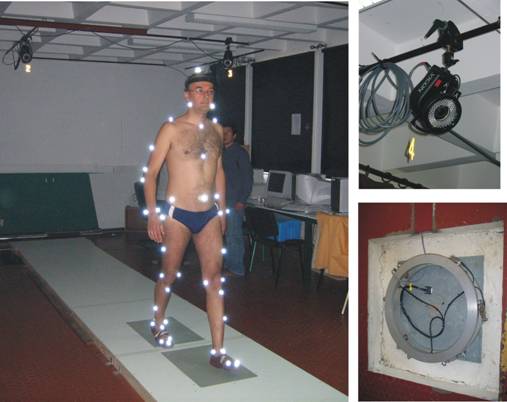

Fig. 1. Experimental measurements with VICON-460 capture motion system in the laboratory conditions: (i) fluorescent markers attached to the human body, (ii) infra-red camera for capturing kinematics, (iii) 6-axes force platform for measurements dynamic reactions.
By use of the MSHUB interface, corresponding generalized coordinates (joint angles and their derivatives) are identified. Considered software enables accurate modeling, off-line simulation and verification of the experimental results. MSHUB enables calculation of the inverse dynamics, i.e. determination of the corresponding joint torques characteristic for the motion observed.
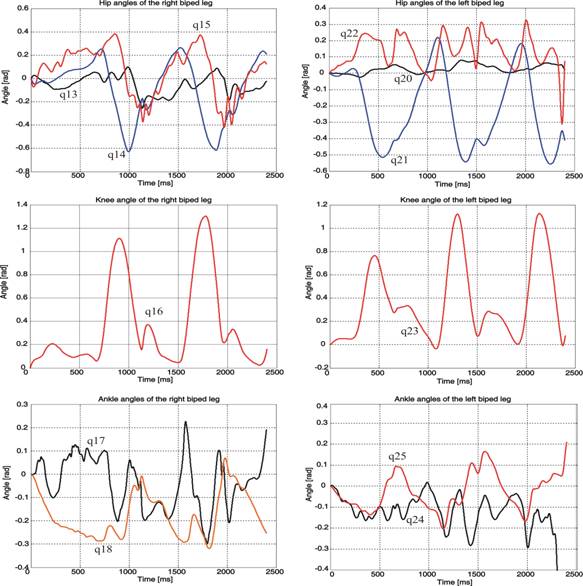
Fig. 2. Identified angles in the particular joints of human legs during locomotive experiment.
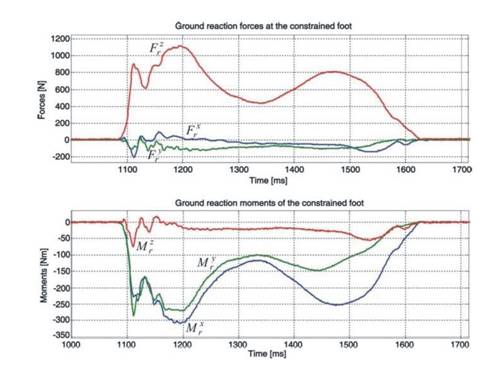
Fig. 3. Experimentally measured dynamic reactions (ground reaction forces and torques) along/around particular axes in sagital (x), lateral (y) and vertical (z) directions at the supporting foot.
Complementary to the experiments with capturing human gait, corresponding measurements with dual-arms/hands manipulation of different objects have been performed in laboratory conditions.
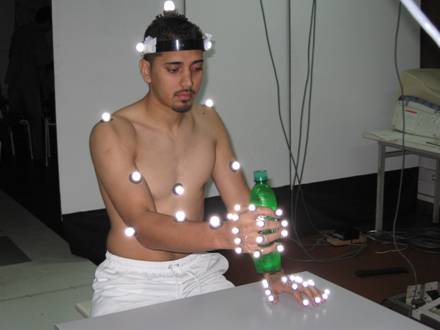
Fig. 4. Capture motion experiments with dual-arms manipulative tasks.
