Research Topic: Bio-Inspired Synthesis of Artificial Human Gait for Biped Robots – Knowledge-Based Generator of Joint Trajectories
The main objectives concern with building of a bio-inspired, artificial gait generator providing referent biped robot trajectories applying advanced learning algorithms of biped robot inverse kinematics.
The input to the designed gait generator represents the anthropomorphic cycloids/trajectories of the feet and hips’ joints (left and right) centers (Descartes coordinates). The corresponding cycloids for one arbitrary real gait are presented in Fig. 1. Multi-layer artificial neural network structure was used for training biped robot’s inverse kinematics, i.e. its lower extremities (legs). The layout of the block scheme of the bio-inspired generator of the artificial gait is shown in Fig. 2. Parameters of the biped robot considered are defined in advance. Open-loop simulation results of a biped robot’s model as well as the experimental data (scaled from the biological system to the robot dimensions) obtained by capture motion system are used as the appropriate training sets for the proposed network structure. Designed knowledge-based gait generator enables synthesis of different anthropomorphic robot trajectories for linear motion, moving slalom (Fig. 3) or circle, climbing stairs, running, jumping, etc. Developed algorithms for trajectory generation are suitable for implementation in tasks of path planning, obstacle and collision avoidance at the strategic control level of biped robots. Designed knowledge-based algorithms ensure bio-inspired, anthropomorphic character of artificial gait since it has experimental background.
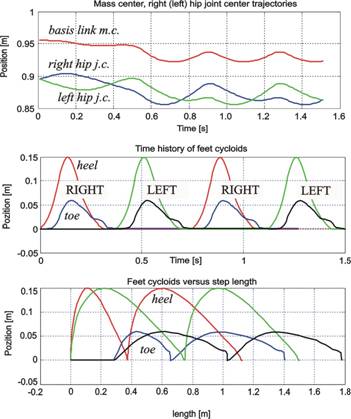
Fig. 1. Example of input signals brought to the learning structure used for off-line training of the inverse leg’s kinematics – anthropomorphic feet and hip joint cycloids as well as trajectory of mass center of the basic link (pelvis link).
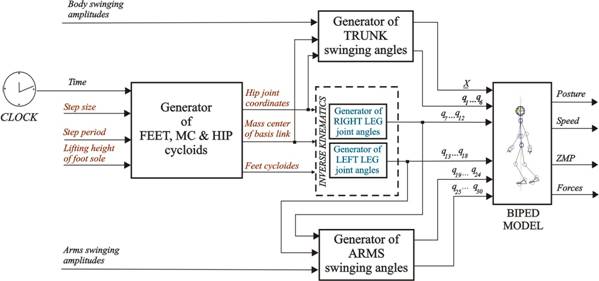
Fig. 2. Block-scheme of the bio-inspired generator of artificial gait for biped robot of an anthropomorphic structure.
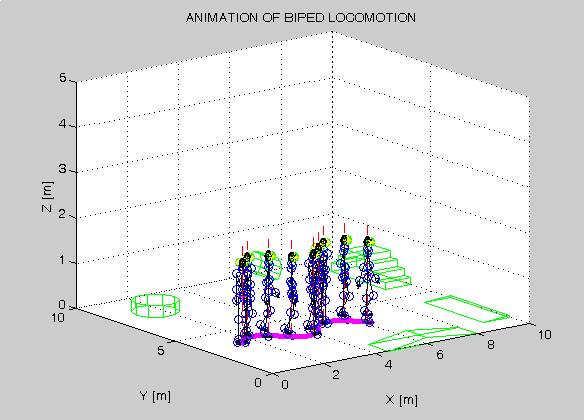
Fig. 3. An example of a slalom trajectory of biped robot with immobile obstacles in its surrounding.
